Models
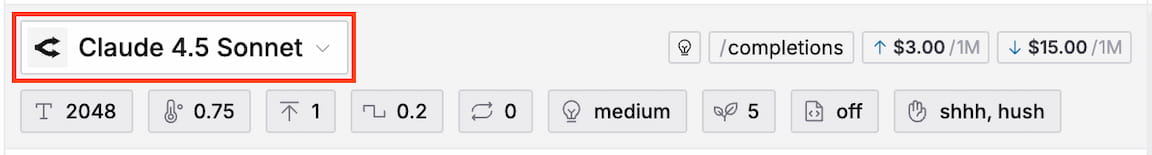
You can select and configure a suitable LLM for each Prompt independently. Just click on the model name at the top of the Prompt detail page to open the model selection dialog and choose from a wide variety of providers and models.
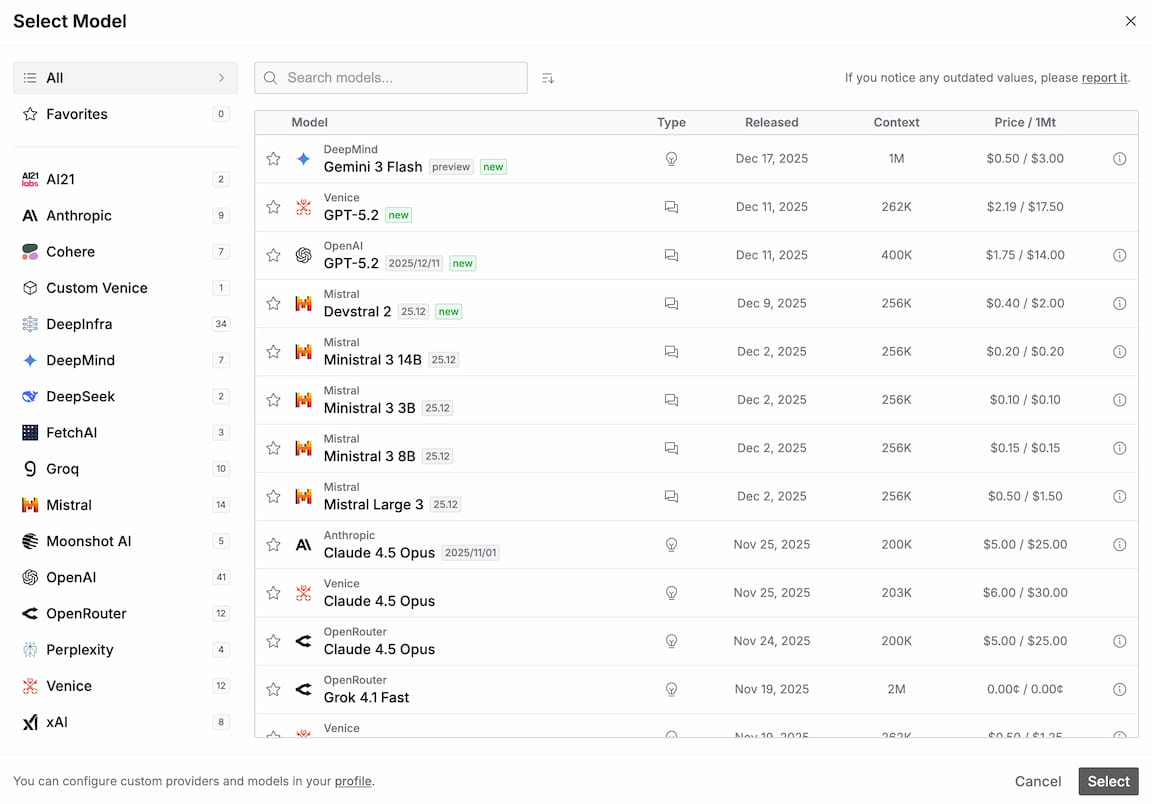
To see the full list of supported models, take a look at the LLM Index.
Related resources
Model Info
To the right of the model selector, you can find a few badges with useful information about the selected model.
Model Type
The model type is simply an internal categorization of the model and has no direct impact on functionality within the app (e.g. settings). Due to the large amount of different architectures of models it is not always straight forward to put them into buckets. Therefore, take this metric as a hint, not as a strict classification.
Options are Completion, Chat, Reasoning, Deep Research, Code
API Format
The API format indicates which LiteLLM endpoint is used for the model.
Currently, only the Completions API is supported.
Token Price
The inference price for input and output tokens is set by each provider and displayed in units of $ per 1 million tokens. There is no markup, inference costs will be the same as if you would use the provider's API directly.
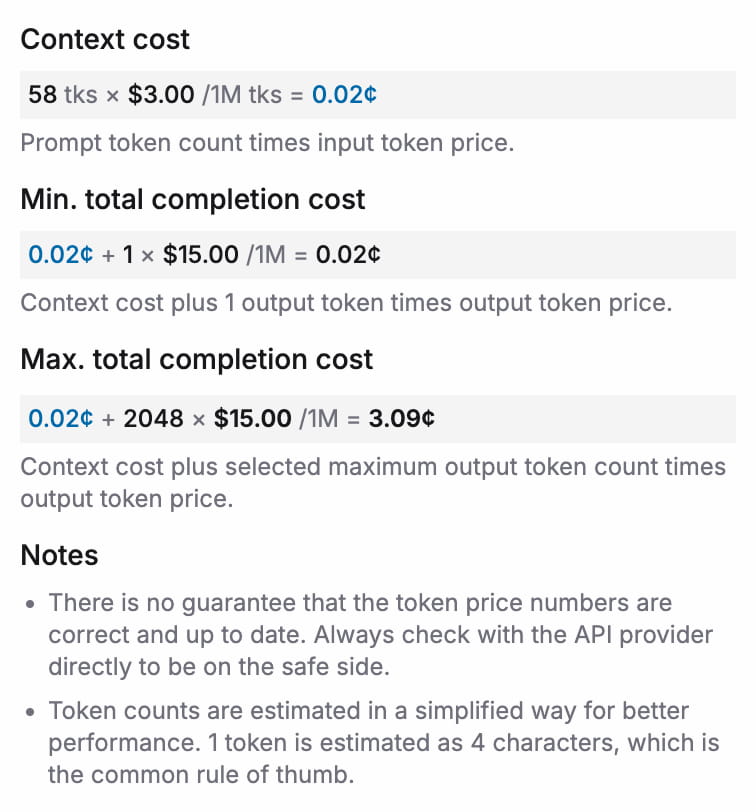
The total completion price is always calculated as
cost = prompt_tokens * price_in ÷ 1M + completion_tokens * price_out ÷ 1MYou can find an estimate for the cost of a single completion at the bottom right of the Prompt Messages tab.
For a detailed breakdown, just hover over it:
Model Settings
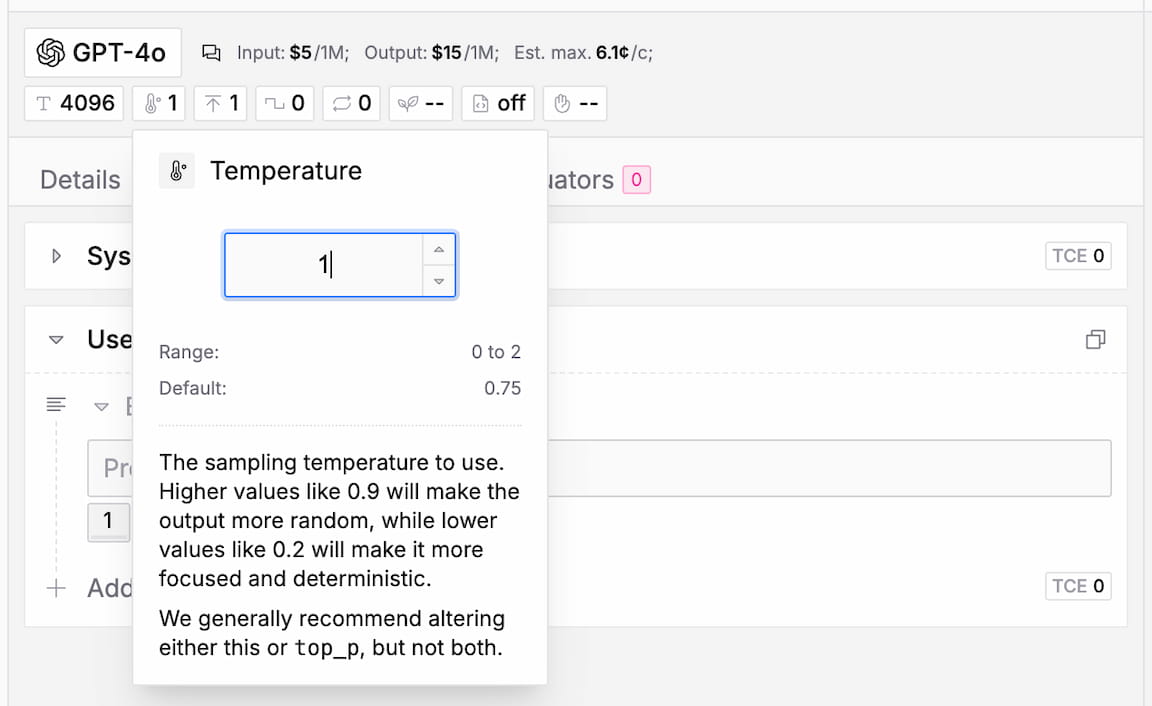
Below the model selection you can tune the model settings. To edit a parameter, just click on it to open its details. The popover lets you adjust the value of the parameter and gives you useful information about the min/max range, the default value, and an explanation of what the parameter does.
If a specific model does not support a setting it will be grayed out and omitted when submitting the prompt to the API.
Token Limit
The maximum number of tokens the model should process/generate in the completion. Unfortunately, different providers treat the token limit differently. Sometimes the token limit refers to input plus output tokens, e.g. OpenAI, and sometimes it refers only to the output tokens, e.g. Anthropic.
The model can never exceed the token limit. So if you experience completion cutoffs, the token limit is most likely the culprit.
Temperature
The sampling temperature to use. Higher values like 0.9 will make the output more random, while lower values like 0.2 will make it more focused and deterministic.
Top P
An alternative to sampling with temperature, called nucleus sampling, where the model considers the results of the tokens with top_p probability mass. So 0.1 means only the tokens comprising the top 10% probability mass are considered.
It is generally recommended to either alter the temperature or the top p parameter, but not both at the same time.
Frequency Penalty
Positive values penalize new tokens based on their existing frequency in the text so far, decreasing the model's likelihood to repeat the same line verbatim.
Presence Penalty
Positive values penalize new tokens based on whether they appear in the text so far, increasing the model's likelihood to talk about new topics.
Reasoning Effort
Reasoning Effort determines how much reasoning the model should do during the completion.
Options: none, low, medium, high
Thinking
Thinking is an alternative to Reasoning Effort, mainly used by the Anthropic API. If supported, you can enable/disable "thinking" for completions and specify a related token budget. If no budget is set, the default of 1024 tokens will be used.
Models support either Reasoning Effort or Thinking, never both.
Web Search Options
If the model supports it, you can specify the Search Context Size under Web Search Options. This allows the model to access the internet during completions for up-to-date information.
Options: low, medium, high
Seed
If specified, the model will make a best effort to sample deterministically, such that repeated requests with the same seed and parameters should return the same result. However, determinism is not guaranteed!
JSON Mode
If set to true, the model is forced to output JSON-formatted responses. Note that your prompt has to contain the word "json", otherwise the API will throw an error.
Stop Sequences
A comma-separated list of up to 4 sequences where the API will stop generating further tokens. The returned text will not contain the stop sequence.
Custom Models
We recommend to always use the default provider and model if they are available and your specific workflow supports it. Otherwise, you can define your own custom providers and models under Menu › Account.
Once defined, you can select custom models just like default models in the model selection dialog.
Configuring Providers
You always need to first create a custom provider that holds the base URL for your API. Simply click on "+ New" in the custom provider panel. Everything you need to add is a name for your provider and the base URL of the API.
Custom providers currently follow either the OpenAI or OpenRouter format, depending on the model identifier (see below).
This means the actual endpoint used for requests is {base_url}/chat/completions.
Configuring Models
Once we have a custom provider, we can set up one or more custom models for it. Click on "+ New" in the custom model panel.
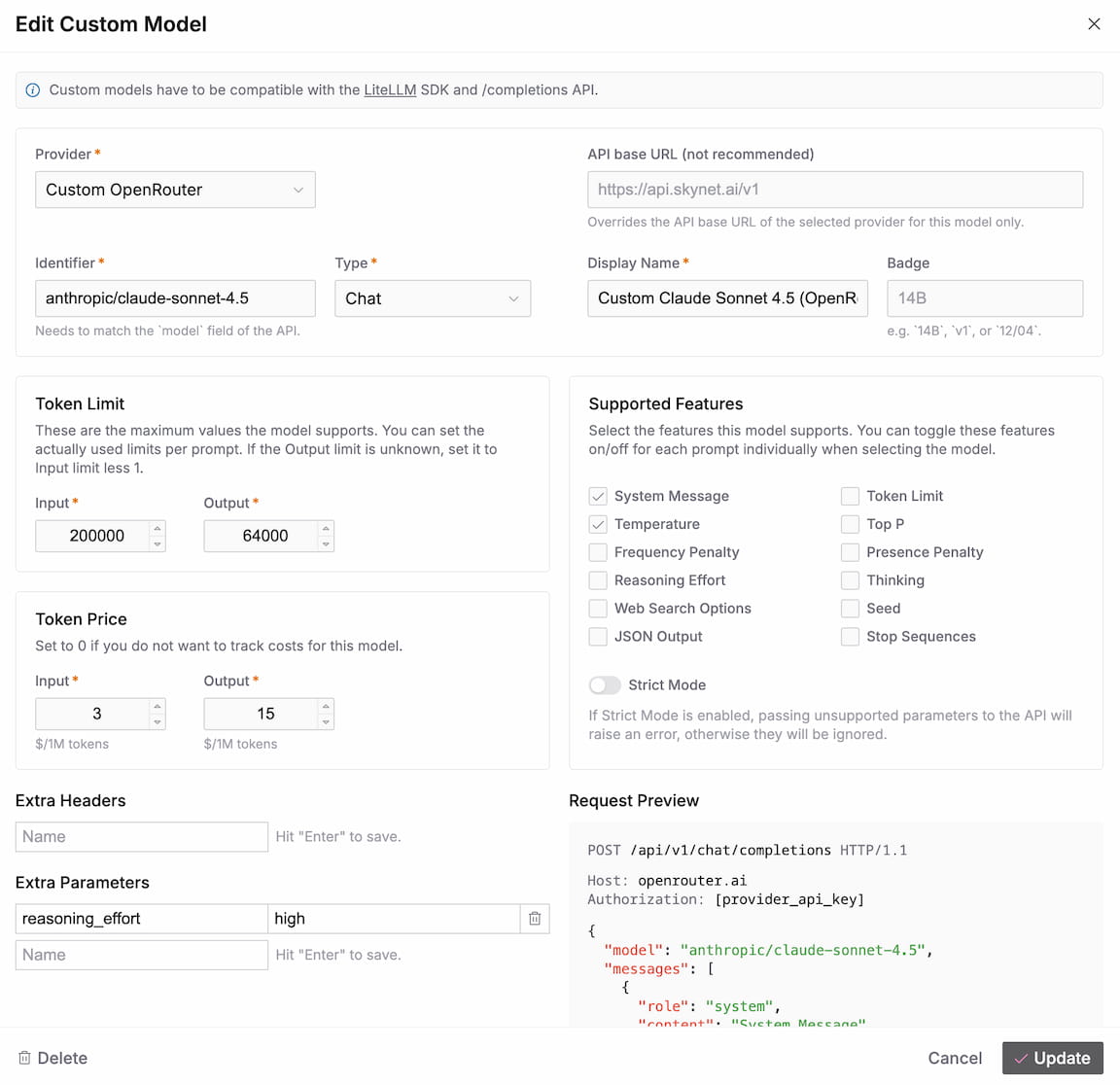
Settings
API Base URL
We do not recommend to use this, but if you absolutely must, this field allows you to override the base URL of the provider for this specific model only. You nevertheless need to select a custom provider.
Identifier
The identifier specifies the model routing within the API. This is the same as for all the standard APIs and maps to the model field in the payload.
Example: gpt-5.2-2025-12-11
Type
See Model Type section above.
Display Name
Used to display the model within the app, otherwise no function.
Badge
You can use this to specify a variant of a model, e.g. 14B, v1, or 12/04. The badge is displayed wherever the Display Name is used.
Token Limit
See Token Limit section above.
Note that this defines the maximum limits the model supports. When using the model, you can still adjust the limits per Prompt, up to the maxima defined here.
Token Price
See Token Price section above.
The token price is used to estimate inference costs when using this model. If this does not apply or if you do not want to include the model's inference cost in the estimation, just set the values to 0.
Supported Features
Flags to define which features the model supports. If you activate a feature here, a corresponding setting will be available for the model when you select it for a Prompt.
To get an idea how the features map to actual request parameters, take a look at the completion() method in the LiteLLM documentation.
Strict Mode
Determines whether or not parameters are validated against LiteLLM's internal model settings map. If Strict Mode is activated and an unsupported parameter is passed, you will receive errors during completions. We recommend to turn Strict Mode on by default and only turn it off if you encounter errors.
Extra Headers
Allows you to pass extra headers through to the API, e.g. for authentication or tracking.
Extra Parameters
Allows you to pass extra parameters through to the API. The inputs are automatically converted to boolean, number, string, or object types. If you want to pass a boolean, or number as a string, you can just wrap it in quotes, e.g. "true", or "42".
Request Preview
Below the settings, the app gives you a preview of how a sample request would look like with your configuration. If you encounter issues, you can compare this to how requests should look like for your setup.
If you have trouble getting your custom models to work, just get in touch.